By Joe Berk
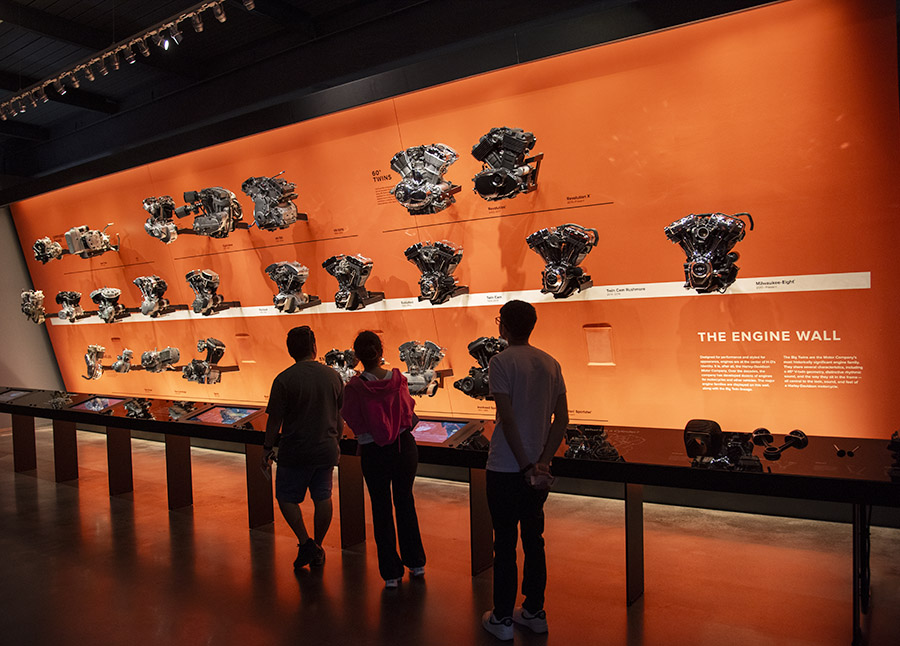
Love them or hate them, there’s something about Harley-Davidson motorcycles that command attention, and during our recent visit to the Harley museum in Milwaukee, one of the exhibits that grabbed my attention was The Engine Wall. It had a magnificent display of Harley-Davidson engines including their big twins, their small twins, and other engines in the Harley family tree. I always found the evolution of the big twin engines mildly confusing, but this dramatic display cleared all that up. I grabbed a photo of each one and I thought I’d share them with you here on the blog.
F-Head (1911-1929)
The F-head engines were 61 cubic inches, and later, 74 cubic inches. These were Harley’s first v-twin engines, and they featured an inlet over exhaust valve configuration. What that means is that the intake valve was an overhead valve contained in the cylinder head (it moved down to let in the air-fuel mixture), and the exhaust valve was a side valve (or flathead valve) contained in the cylinder on one side (it moved up to allow the exhaust gases to escape). Inlet over exhaust internal combustion engine configurations (or F-heads) were fairly common in the early days of gasoline engines. If you draw the arrangement schematically, it sort of looks like an F (hence the name). The larger of the two Harley F-head models produced 11 horsepower.
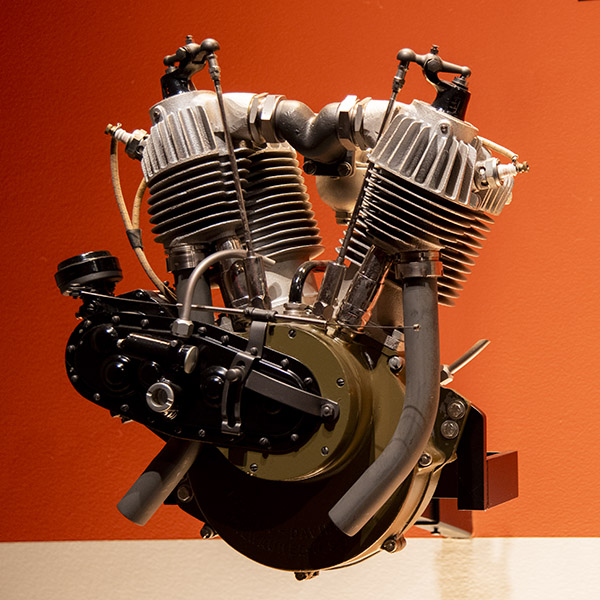
V-Series Flathead (1930-1936)
The V-series flatheads were either 45 cubic inches or 74 cubic inches. They were sidevalve engines, which means the valves and their seats faced up and were located in the cylinders (not the cylinder heads), alongside piston (hence the sidevalve descriptor). This allowed the head to be basically flat (when viewed from the bottom), and that’s why these engines are called flatheads. It’s an old school design and it works well, but due to the twists and turns the intake and exhaust gases have to make and their poor heat dissipation, flatheads are limited in how much power they can produce. Harley would get around to fixing that in 1936 with the introduction of their overhead valve Knucklehead engine, but that would be down the road. Read on; we’ll get to that.
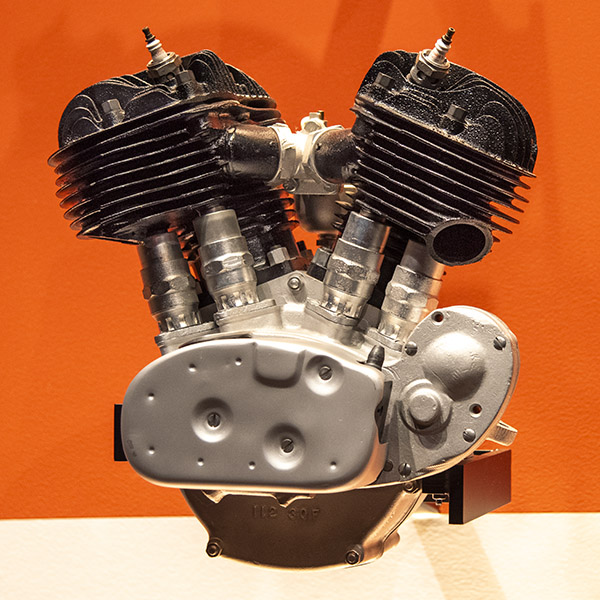
U-Series Flathead (1937-1948)
This was the second iteration of Harley’s sidevalve (or flathead) engines. There were two versions: The U and UL models (both had 74 cubic inches), and the UH and ULH (these had 80 cubic inches). The U series of engines were used for both motorcycles and Harley’s three-wheeled vehicles.
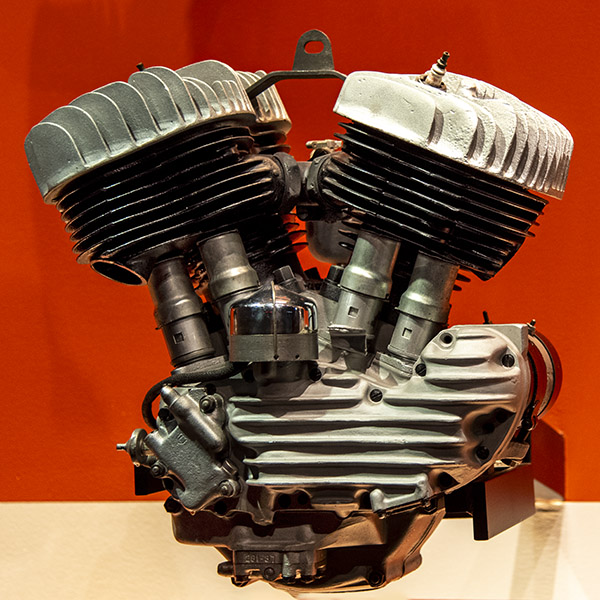

Knucklehead (1936-1947)
The Knucklehead was the first of Harley’s overhead valve engines, and the knucklehead name was derived from the valve covers’ appearance. Knuckleheads were made in a 61 cubic inch model and then in 1941, a 74 cubic inch configuration.
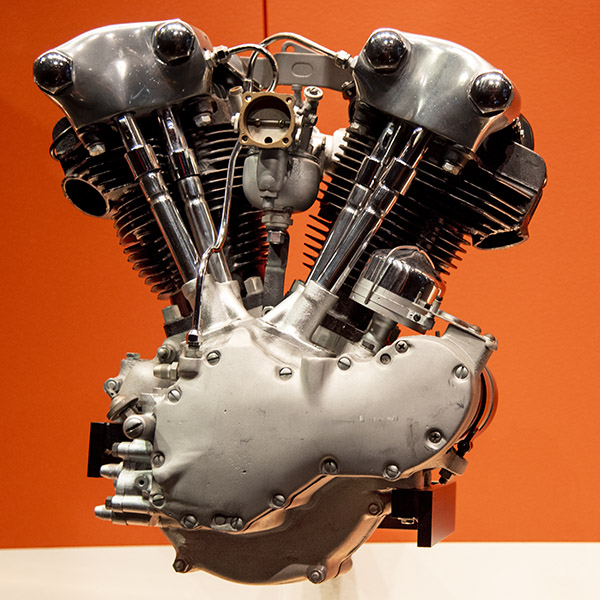
I’ve read that Knucklehead engines had serious oil leak issues caused by an overly complex rocker box cover (something Harley tried to correct with the next engine configuration, the Panhead). Knuckleheads had cast iron cylinder heads, which tended to make them run hot (cast iron does not dissipate heat very well). The Knucklehead motorcycles were the first Harleys that featured their distinctive Big Twin style, something that Harley has kept right up to present-day offerings.
Panhead (1948-1965)
The Panhead Harleys got their name from the valve covers’ appearance (they look like pans). This engine and the Evo engine (the engine that appeared two iterations later) are, in my opinion, the two best looking engines Harley ever made. In a major design shift for Harley, Panhead cylinder heads were made of aluminum, which improved heat dissipation and temperature control. The Panhead was intended to improve performance and address the oil leak issues associated with the Knucklehead. Did it work? I don’t know. I’ve never seen a Panhead Harley that did not leak. They sure are beautiful, though. The Panhead had a short production run, but it had a major impact on Harley styling.
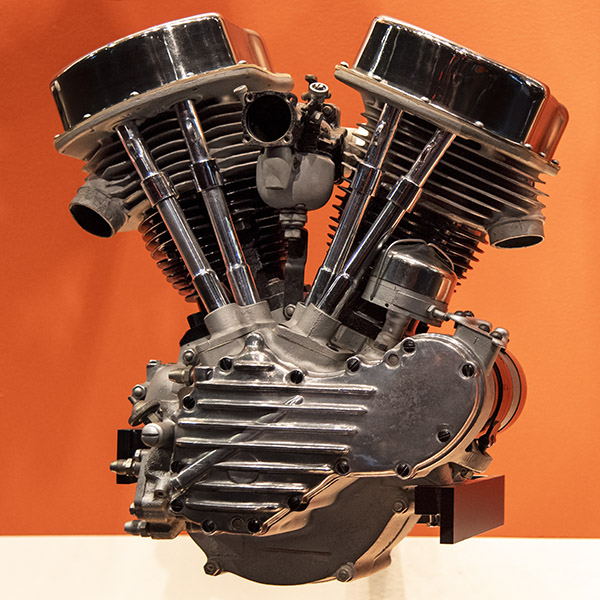
The last year of the Panhead (1965) was the first year Harley had electric starting (that was when Harley introduced the Electra Glide name). My two ultimate dream bikes are the 1965 Harley Electra Glide and the Norton P-11 (which is discussed elsewhere on ExNotes). In my opinion, Panhead Harleys are exceptionally beautiful motorcycles.
Shovelhead (1966-1984)
1966 saw the introduction of another Harley engine, and yet another name based on the rocker box appearance.
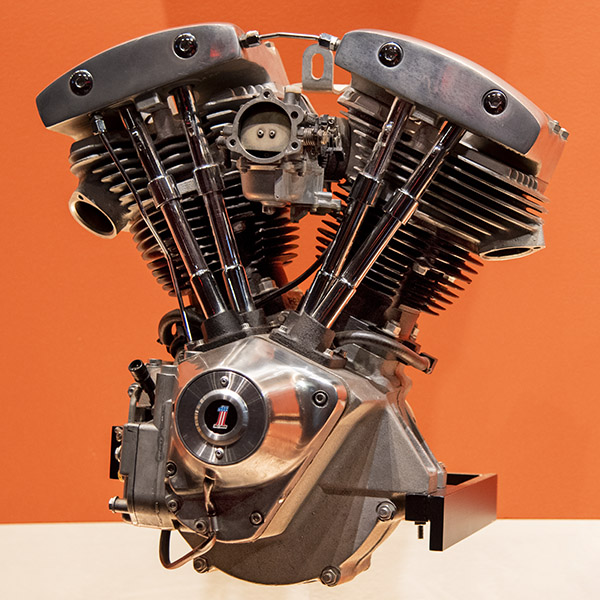
I had a Shovelhead (a 1979 Electra Glide Classic). It was so bad I called it the Optical Illusion (because it looked like a motorcycle). My shovelhead Electra Glide was the worst motor vehicle of any type I ever owned (car, motorcycle, lawn mower, and Cox-.049-model airplane). It was constantly plagued by oil leaks and breakdown. It wouldn’t go a hundred miles without something breaking. After coming off a Triumph Bonneville, the Harley handled like a garbage truck. It would hang an exhaust valve every 4,000 miles, and as it was explained to me by the dealer, it was because when unleaded gasoline was introduced in the US, the valves would stick in the valve guides without the added lubricity provided by leaded gas. I don’t know if that was the reason or not, but in 12,000 miles, that bike needed three valve jobs (the first two were on the dealer with the bike’s 12,000-mile warranty; the third was on me because the bike had just over 12,000 miles. After paying for that last valve job, I sold my Electra Glide and I swore I’d never buy another Harley (but I did; see below). It was beautiful, though, and I wish I had kept it.
Evolution (1984-1999)
Harley got their act together on this one, and it was probably because they subcontracted the engineering to Porsche. Willie G drove a Porsche, and he knew they knew how to engineer engines. It was a good move. I had a ’92 Heritage Softail and it was a great motorcycle. My dealer? Not so much, but I guess it was all part of the Harley experience. I put a lot of fun miles on my ’92 including trips all over the US Southwest and Mexico, and I enjoyed riding it. The engine style was great, too.
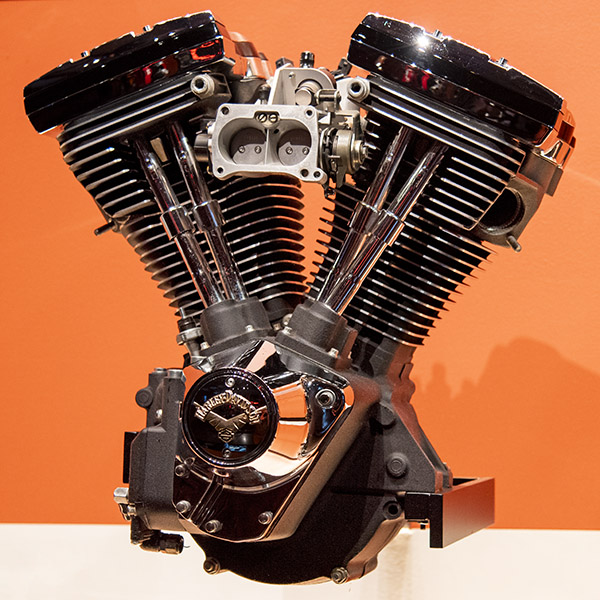

In my opinion, the Evo engine was one of the two best-looking motors Harley ever made (the other was the Panhead; see above).
Twin Cam (1999-2017)
The thing most amazing to me about the Twin Cam engine was that Harley kept it as long as they did. It was basically a bust. Plagued by mechanical failures and overheating from the get-go, one had to be either ignorant or a masochist to buy a Harley with a Twin Cam motor. Cam failures, lubrication failures, and overheating were a fact of life if you owned one of these. The rear cylinder overheating issue was so bad that Harley incorporated a switch and an automated feature to shut down the rear cylinder if the engine got too hot. Amazingly and amusingly (at least to anyone with any mechanical smarts), Harley called activation of the rear cylinder shutdown feature their “parade mode,” with the implication that it was intended to accommodate riders who rode in, you know, parades. There were kits available to shield the riders’ legs from the intense heat the rear cylinder generated.
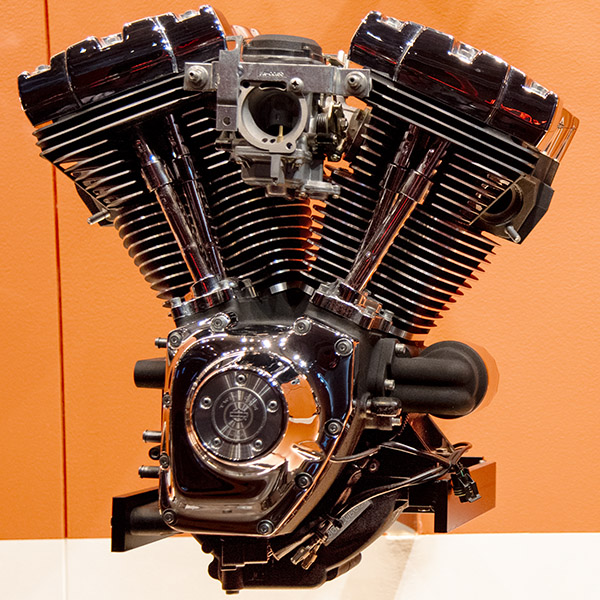
Twin Cam Rushmore (2014-2016)
This is a higher performance version of the Twin Cam engine that involved many changes, the most significant of which was liquid cooling for the cylinder heads on the Ultra Limited, CVO Limited, and Tri-Glide models (the models in which the radiators could be hidden; you can’t have a Big Twin Harley looking like a Gold Wing, I guess).
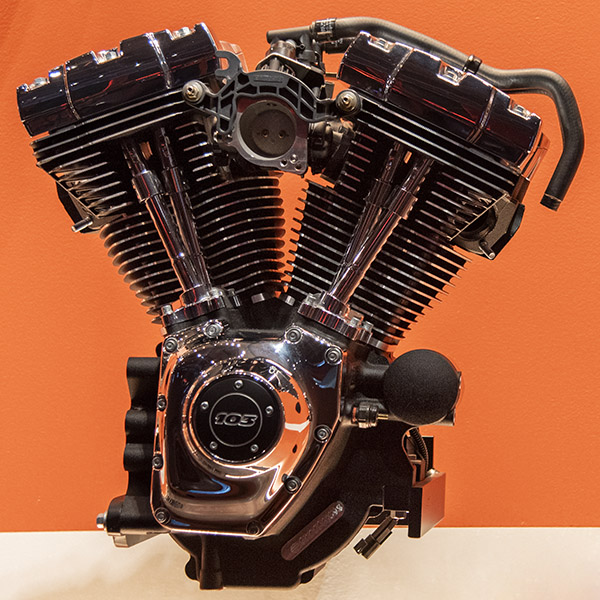
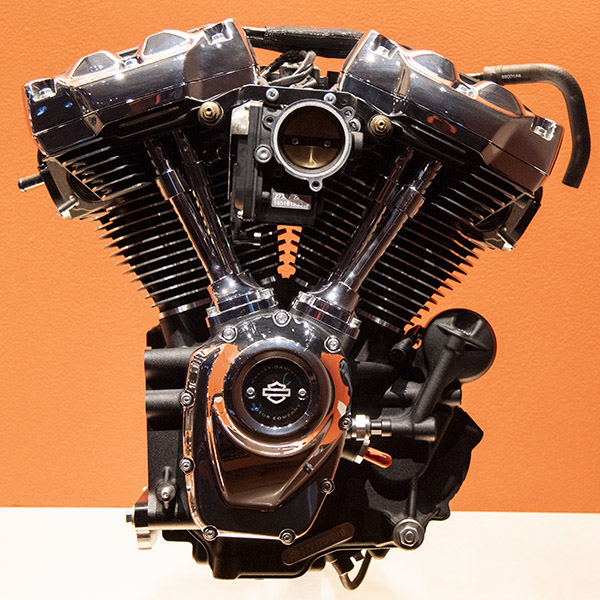
Milwaukee Eight (2017 to Present)
Harley joined much of the rest of the world in 2017 when they incorporated four valves (two intake, two exhaust) for each cylinder. Let’s see…two cylinders, four valves per cylinder…that makes eight, and Harley’s hometown is Milwaukee. Hey, the Milwaukee Eight! (At least the name makes more sense than the Rushmore mentioned above.) These engines had problems and Harley had recalls to address them. Wet sumping was a major issue, as was overheating. The Milwaukee Eight incorporated a plastic intake manifold, too, which also had issues. I like the name, though.

I thought the Harley Museum’s Engine Wall was very, very well done. Harley put a lot of thought and work into it, and as a mechanical engineer and former Harley owner, I enjoyed it. There’s the obvious: the actual engines on display. And then there’s the subtle: the slight tilt of that orange wall toward the visitors so that the engines were presented not an angle, but straight on as you tilt your head up to view the different engines. The colors are classic Harley: black, orange, and chrome. It’s one of the better displays I’ve seen of any type in any museum. The whole thing just works. Harley got The Engine Wall right; they did an awesome job.
As mentioned at the start of this blog, there were more engines on The Engine Wall. These included their smaller engines (for the Sportsters and the racebikes), their singles, and some interesting other twins. Keep an eye on ExNotes; we’ll show those, too.
Never miss an ExNotes blog:


