 Unlike motorcycles, I’m not fixated on doing things the old way for electrical energy storage. I run a lithium-polymer battery
Unlike motorcycles, I’m not fixated on doing things the old way for electrical energy storage. I run a lithium-polymer battery in the Husqvarna that has exceeded all my expectations. The thing never goes dead (no trickle charger needed) it has tons of cranking amps (no need to use the compression release to start the bike) and it weighs nothing. You can install the thing in any position and nothing will leak out. The only drawback to the lithium-polymer battery
is cost.
 Battery technology is advancing rapidly with so many new combinations of lithium with something else, molten salt or rare elements only found in war torn areas. It’s hard to know which technology will win out in the end but for now, in my solar-powered shed system, lead-acid still offers the best electron storage option.
Battery technology is advancing rapidly with so many new combinations of lithium with something else, molten salt or rare elements only found in war torn areas. It’s hard to know which technology will win out in the end but for now, in my solar-powered shed system, lead-acid still offers the best electron storage option.
Lead-acid batteries are messy, inefficient and half their capacity comes at a voltage too low to run your equipment correctly. They are heavy as hell and the cable connections are always corroding from the acid fog and hydrogen fumes escaping from the fill caps. You’re lucky to get 5 years service out of a lead-acid battery. The things are problematic in most every way.
But not in all ways: lead-acid is a completely mature technology. We’ve been building them since 1860 and there is a cradle-to-grave recycling system in place right now. Any auto store or Wal-Mart has the ability to take your old lead-acid batteries and deal with them responsibly. Unlike the new battery elements there are no ecological surprises with lead-acid: We know all.
Lead-acid batteries are available everywhere. Go to any town in the world with at least one gas station and you can buy a lead-acid battery. You don’t have to deal with Tesla or any of the high-tech battery startups that don’t actually have product. Your battery isn’t tracked online, the software will never need to be updated and your battery bank will never be monitored by anyone but you. Unlike most e-car and e-bike batteries, lead-acid batteries come in standard sizes (24, 27, 31, 4-D, 8-D) and for the most part are interchangeable unless you have a restrictive battery box or short cables.
Lead-acid batteries are tough. It’s hard to damage a clean lead-acid battery with tight connections. They put out gobs of amps on demand and as long as there is electrolyte in the cells they stand up to overcharging well. They’re even somewhat repairable: Go on YouTube and look up battery repair for ways to flush out debris from old lead-acid batteries to gain new life.
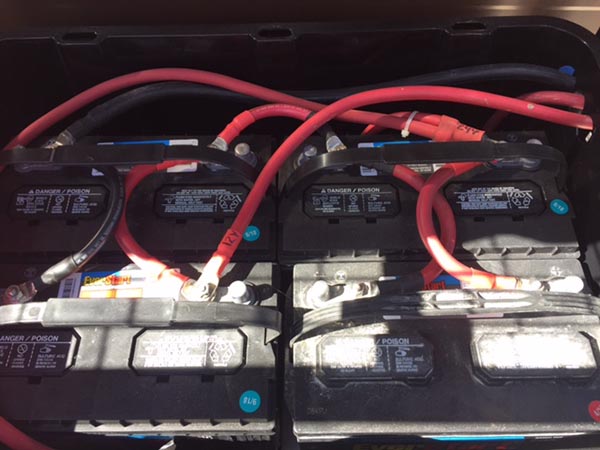 Lead-acid batteries are easily scalable and nearly any voltage or amperage desired can be achieved with large, simple jumper cables. I’m running 4, group 31, 12-volt batteries in my 24-volt system. My future plans are for 16 batteries total but there’s no rush. I can take as long as I want to get there or 8 batteries might prove to be enough for my usage level.
Lead-acid batteries are easily scalable and nearly any voltage or amperage desired can be achieved with large, simple jumper cables. I’m running 4, group 31, 12-volt batteries in my 24-volt system. My future plans are for 16 batteries total but there’s no rush. I can take as long as I want to get there or 8 batteries might prove to be enough for my usage level.
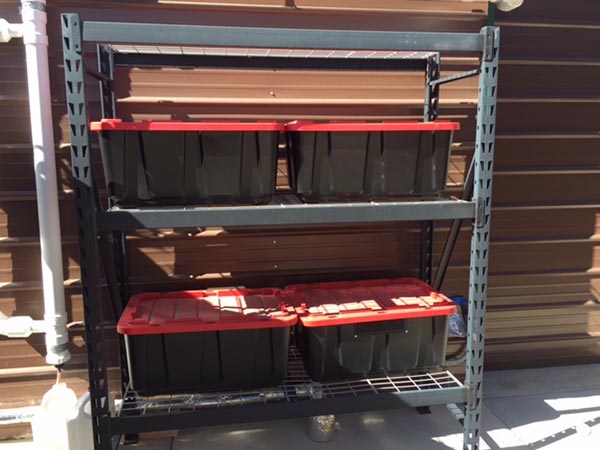 Most important for me: They are cheap! The four deep cycle marine batteries in my off-grid system @100 amp/hour each give me a total of 2400 watts of storage (@ 50% capacity) for 400 dollars. If I ever get to 16 batteries I’ll have 9600 watts of storage for around 1600 dollars. Compare that to 7000 dollars for 7000 watts of storage from Tesla’s Powerwall.
Most important for me: They are cheap! The four deep cycle marine batteries in my off-grid system @100 amp/hour each give me a total of 2400 watts of storage (@ 50% capacity) for 400 dollars. If I ever get to 16 batteries I’ll have 9600 watts of storage for around 1600 dollars. Compare that to 7000 dollars for 7000 watts of storage from Tesla’s Powerwall.
The newer Powerwall is AC-in, AC-out and comes with a built-in AC inverter which is a savings if you’re charging from the grid but you’ll need a solar AC inverter to charge the Powerwall from the sun so it’s kind of a wash for my set up. The lifespan/charge cycle of lead-acid batteries is supposed to be less, judging from the two-year lifespan of the lithium ion batteries used in my cordless tools, maybe not.
 I’m not a Luddite when it comes to battery technology on motorcycles or power tools but for me the new designs and materials haven’t yet made sense for large, stationary storage banks at low cost. I’ll revisit the topic if Tesla reduces the price of their Powerwall by half or some new manufacturer comes up with a wiz bang combination of chemicals that outdoes ancient lead acid technology.
I’m not a Luddite when it comes to battery technology on motorcycles or power tools but for me the new designs and materials haven’t yet made sense for large, stationary storage banks at low cost. I’ll revisit the topic if Tesla reduces the price of their Powerwall by half or some new manufacturer comes up with a wiz bang combination of chemicals that outdoes ancient lead acid technology.
