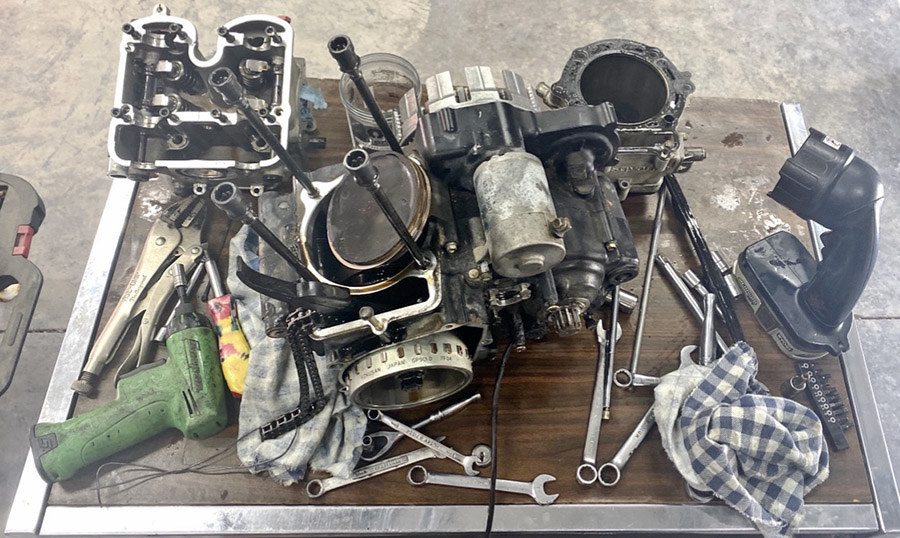
In the first episode of Grind Me A Pound Of Reverse I contemplated buying a Suzuki DR650 and leaning the broken down Husqvarna SMR510 on the side of the shed to bleach in the harsh New Mexico sunlight. Suzuki DR650s are as stone axe simple as you can make a motorcycle today. They are air-cooled, carbureted, have zero electronic widgets (except for ignition) and cost around $6000 for a 2022 model. I’d have to sell a few of my clunkers to fund the DR but it’s the sensible thing to do.
The thing is, the Husky is such a fun bike to ride I thought I’d take a poke at fixing its transmission woes. The Husqvarna crankcase is a vertically split unit which is easier to manufacture but means the entire engine must be dismantled to access the gearbox. In my case this is not a big deal because when a gearbox explodes you have to clean out all the microscopic and not so microscopic bits of metal.

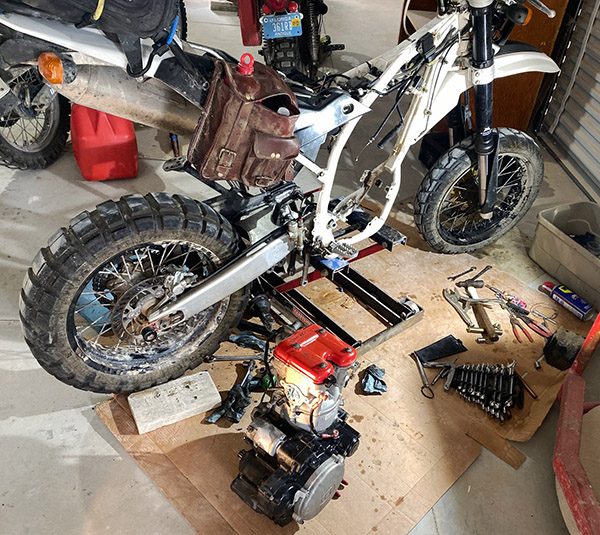
The SMR510 frame is wrapped tightly around its engine and a lot of stuff has to be dismantled to get the lump out into the open. With long-travel suspension causing wide variations in chain tension its best to keep the swing arm pivot as close to the countershaft sprocket as possible. On the SMR the pivot bolt goes through the back of the engine and that means the swing arm has to come off. In addition, the radiators, fuel injection body, EMS and other body parts must be removed also. It took me about 4 hours to finally free the Husky’s engine but I don’t work fast.
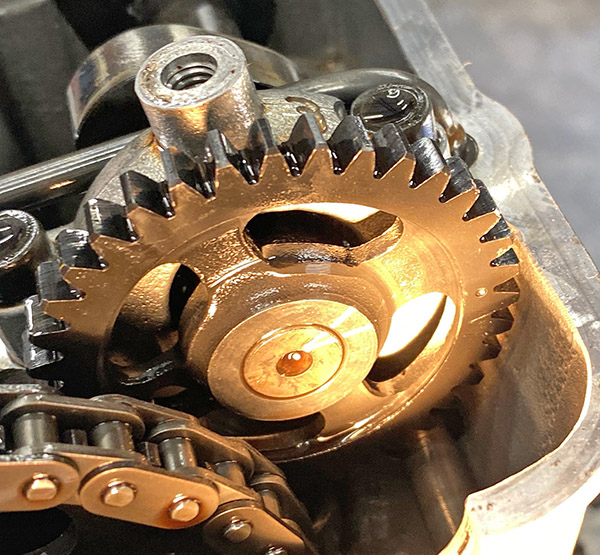


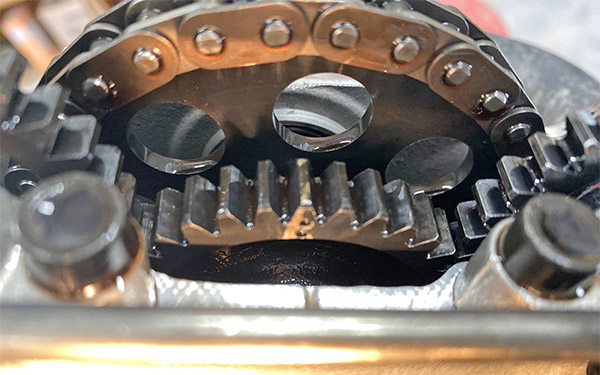
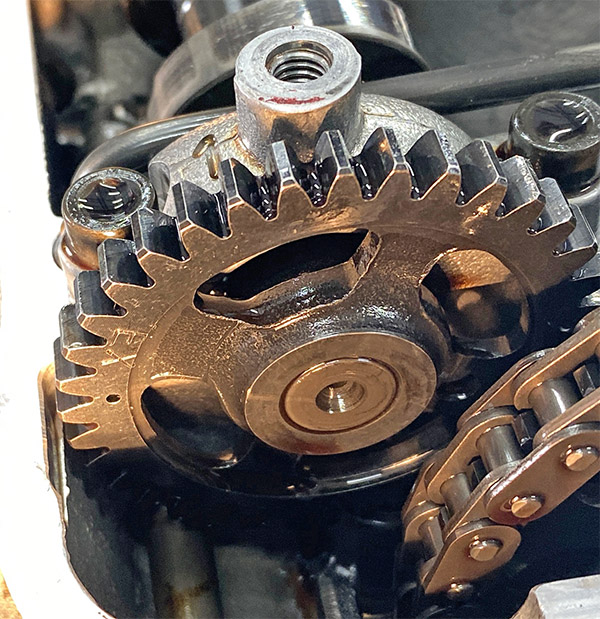
I have no shop manual for this bike so with the engine on the bench the first thing I did was rotate the engine to top dead center-compression stroke in order to find the cam timing marks. The Husky has a cam chain that spins an idler gear; the idler gear then spins the two overhead cams. Each cam has a small dot that lines up with the outside gasket surface of the head. The idler gear has three markings, the center mark is two dots and these dots line up with a mark on the cylinder head.
I also put an additional punch mark on the crankcase and alternator rotor to make finding top dead center less subjective. The Husky’s timing looks pretty easy to do so I’m sure I’ve got it all wrong and the valves will bend the first time I try to start the engine.

Next I removed the cam caps. The cam caps were secured by these allen-head bolts and they were so tight the heads rounded out on three of them. I had to use a flat chisel to knock the bolts loose so I’ll need to get replacements from the hardware store. The head bolts are 10mm allen-type and deeply recessed so once the cams were out of the way I had to cut a 10mm allen wrench to make a long reach socket. The head bolts didn’t round out.
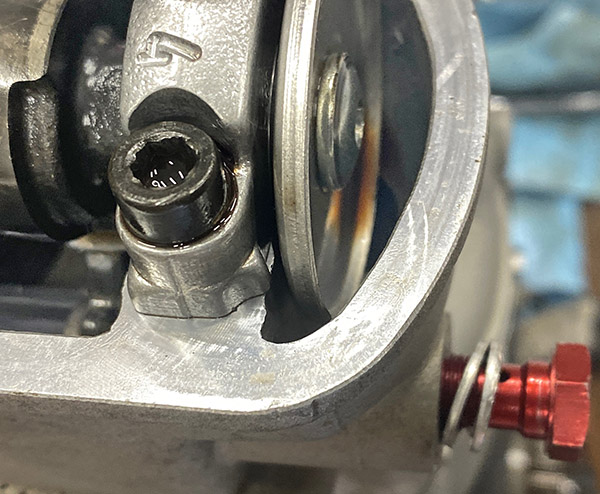
One of the reasons the Husqvarna 510 engine doesn’t last long is the slipper piston. This type of piston is pretty much a racing piston and has so much cut away there is only a narrow skirt to take side loading and a limited surface area for an oil film. The valve train is state of the coil-spring art: long, skinny valves at a narrow angle to give an almost flat-top combustion chamber.
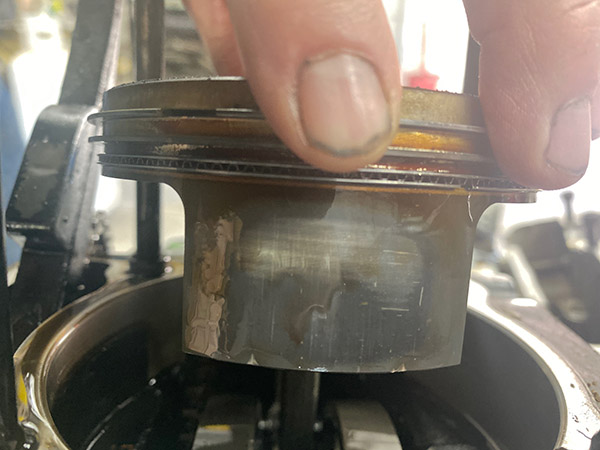

The Husky incorporates small finger-rocker followers to remove valve-stem side loading. The cam lobes swipe across the followers, not directly on the valves. This set up adds a bit of weight to the valve train but the Husky revs to 10,000 rpm without valve float so I’m not going to worry about weight. A nifty feature is the spring-metal separator clip that can be removed from the rocker arm shafts, which will allow the finger rocker to slide over giving access to the valve shims. This means you don’t have to remove the cams to adjust valve clearance.
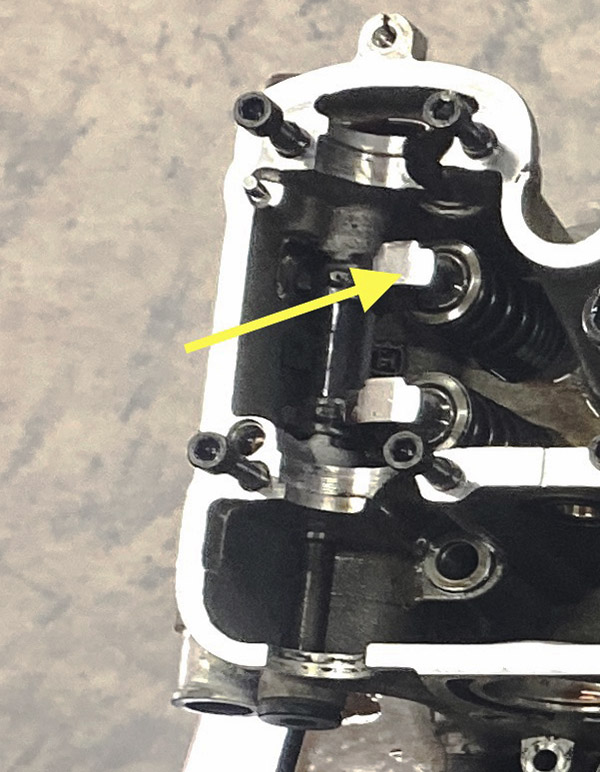
Splitting the cases was a fairly straightforward operation except for the shift drum. I managed to get the thing apart but still haven’t figured out how the shift drum is held into the right crankcase half. I got pretty frustrated and gave it a few whacks but it didn’t budge. I’ll study the situation after I calm down.
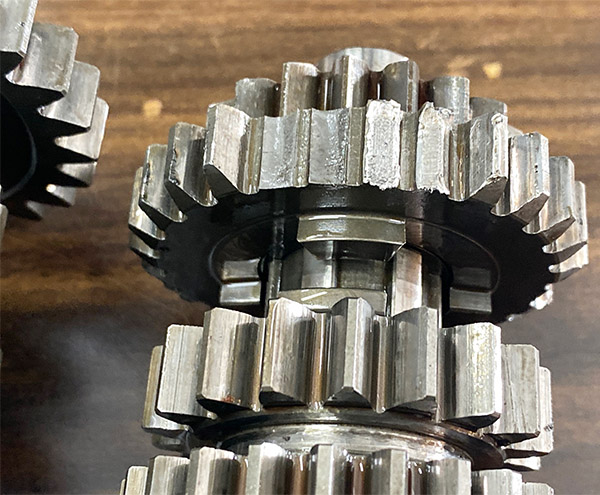
This is what was causing the racket. A couple gears are missing teeth and who knows what other unseen damage to the cluster was done as the bits of hard metal flew around inside? The shift forks may be bent because the bike wouldn’t stay in neutral and kept going into gear when i pushed it around the shop. I decided to get a used gearbox and replace the entire transmission.

The 2008 Husky SMR510 is one of the last Husqvarna’s with a tangible connection to the original Swedish manufacturer. Employees from old Husqvarna operated the company that built my bike. They purchased the name and relocated manufacturing to Italy. Cold, icy Sweden or warm, sunny Italy, who wouldn’t move? Shortly after my bike was built Husqvarna was sold to BMW and the bikes became re-badged BMWs. This only lasted a few years until KTM bought Husqvarna from BMW and the bikes became re-badged KTMs.
So parts are sort of hard to find. I located this complete TE510 (the enduro version of my bike) transmission in England for $285. Shipping was expensive but it’s a long way to Old Blighty and probably one gear would cost $100 if I bought it new. Hopefully it will fit.
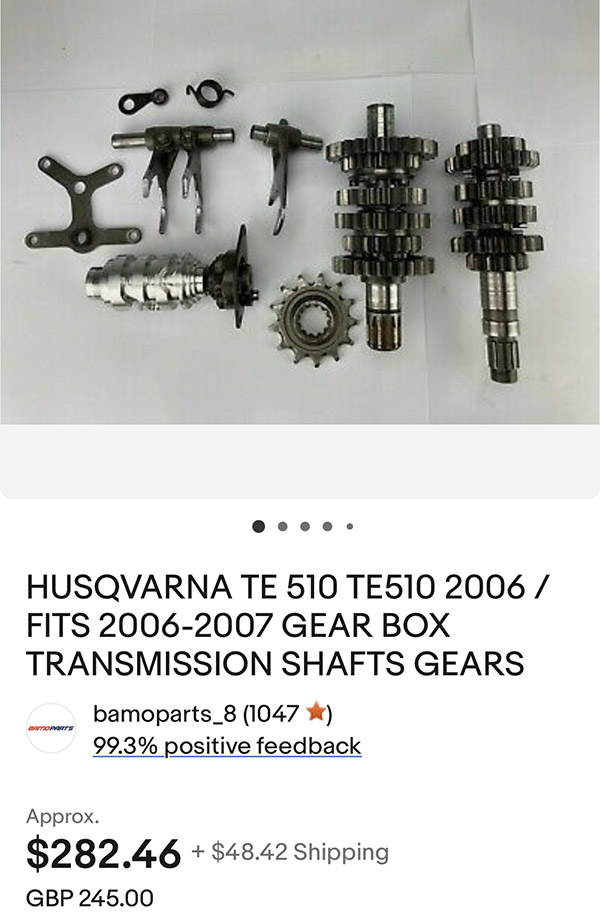
EBay also had a top end gasket set for fairly cheap so I have that kit on the way. The case halves are sealed with goop, no gasket needed. The side cover gasket and alternator gasket came away without tearing so being ever thrifty I can reuse those gaskets.

I’ll have to do a thorough job of cleaning out the transmission debris inside the engine and whenever this stuff arrives I’ll try to reassemble the mess. ExhaustNotes will have up to date information as this project moves forward. Even if the Husky manages to run again I still might buy that DR650.
You know what to do. Share this post and please, do a friend a favor: Hit those pop up ads!
Never miss an ExNotes blog:
Join our Facebook page.

