By Joe Berk
Half a lifetime ago I was a yuppie, and the symbols of being a successful yuppie included an MBA and a Rolex. The Rolex was easy (the only requirement was having more money than brains). The MBA was more difficult. It required going back to school, which I did. Getting the MBA definitely gave me a boost. My career at the munitions company was on fast forward; at one point I was the youngest vice president in the Aerojet corporation (then I got fired, but that’s a story for another time). I loved being in the bomb business (business was booming, so to speak), and being a former Army guy, I was in my element.

Anyway, while I was going to night school for the MBA, one of my classes was titled Human Behavior or something like that. The guy who taught it was a Ph.D in one of the soft sciences, and I knew pretty quickly that he leaned way left. That’s okay; in my book you can lean however you want as long as you don’t expect me to agree with you on every issue.
The first night of class the prof had everyone tell the rest of their class their name and what they did. We were all yuppies, we were all young, and we all had good jobs. It made for good entertainment, but I had a feel for how things were going from the first several yuppies who told us what they did and the prof’s reactions and questions. Yep, the guy was a definite leftie. I started to wonder what his reaction would be to me…a guy firmly entrenched in the military industrial complex working for a munitions company.
“So what do you do, Joe?” Dr. WhatsHisName asked.
“Uh, I’m an engineer,” I said, hoping he would leave it at that, but knowing he wouldn’t.
“What kind of an engineer are you, and who do you work for?”
“Uh, I’m a mechanical engineer,” I said. No sense in oversharing, I figured. Maybe he wouldn’t notice I didn’t name my company.
“Who do you work for?”
“I work for an aerospace company.”
“What company, and what do you engineer?” This guy wasn’t going to give up. I liked my job and I liked what I did, but I wasn’t about to tell Jerry Rubin here I supported the Vietnam War.
“I work for Aerojet, and we make a variety of products.” It had become a contest, and I was losing.
“What are your products?” He had me. Time to ‘fess up.
“I do cluster bombs.” There. It was out. I knew the guy was going to call whoever it is you call when you find someone violating the Geneva Convention. The good doctor stared at me for several seconds. The other 30 or so yuppies in the class were dead silent. It was a pregnant pause if ever there was one and we were pretty close to the 9-month mark. Somebody’s water was about to break.
“Does your family know what you do?” he softly asked, speaking almost in a whisper.
“My wife does,” I said, mirroring his subdued tone.
“And how does she feel about how you earn a living?”
At this point, I knew I had to come clean. “Truth be told, Professor, she’s disappointed in me.” I had hoped that would end the discussion, but the guy would not let up. He was a dog and I was the bone. Then I sensed a way out, anticipating what his next question would be.
“What does she say to you?” he asked.
“Well, Doc, like I said, she’s disappointed, and she’s made that known on several occasions.” The good Professor was nodding knowingly. He was hearing my confession. I don’t recall specifically, but I’m pretty sure he was smiling. I was on a roll and I continued. “You see, Professor, my wife works for TRW’s Ballistic Missiles Division. They do nuclear intercontinental missiles and she’s always asking me why I’m wasting my time screwing around with conventional weapons. If you’re going to go, she always says, go big. Go nuclear.”
My yuppie classmates started laughing. Me, I was scared. I was running a perfect 4.00 grade point average in the MBA program up to that point, and I thought I had just blown any chance of aceing this course. The professor nodded without expression, made a note on his pad, and went on to the next yuppie. My being a wiseass had earned a good laugh, but that note he made couldn’t have been a good thing and I was afraid it would cost me.
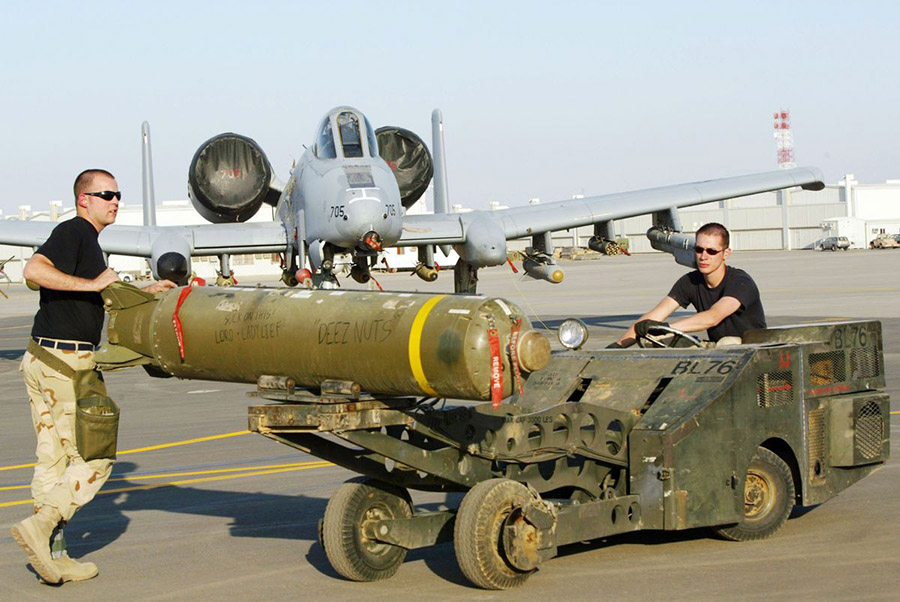
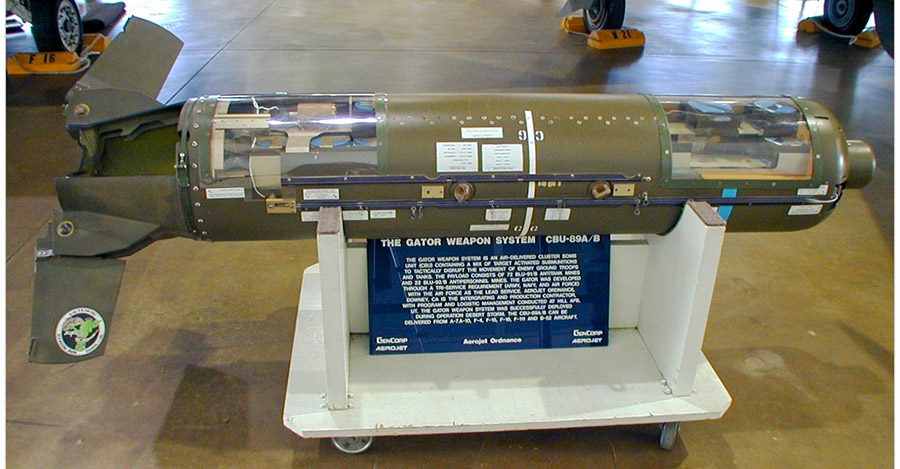
So how did it turn out? I busted my chops in that course and I got my A. But I was sweating bullets for the rest of the term. Little, non-nuclear bullets, but bullets nonetheless. More importantly, the cluster bombs I helped engineer won the Gulf War a few years later in 1991. Most of Saddam Hussein’s Republican Guard tanks were taken out with CBU-87/B cluster bombs and GAU-8/A 30mm ammo (and my company, Aerojet Ordnance, also made the ammo for those A-10 Gatlings). Sometimes when studying human behavior, the guys who know (I mean, really know) reach the only conclusion and solution possible: An adequate quantity of high explosives delivered on target. I’m not at all embarrassed about having had a hand in that. Fact is, I’m proud of it.
Never miss an ExNotes blog: